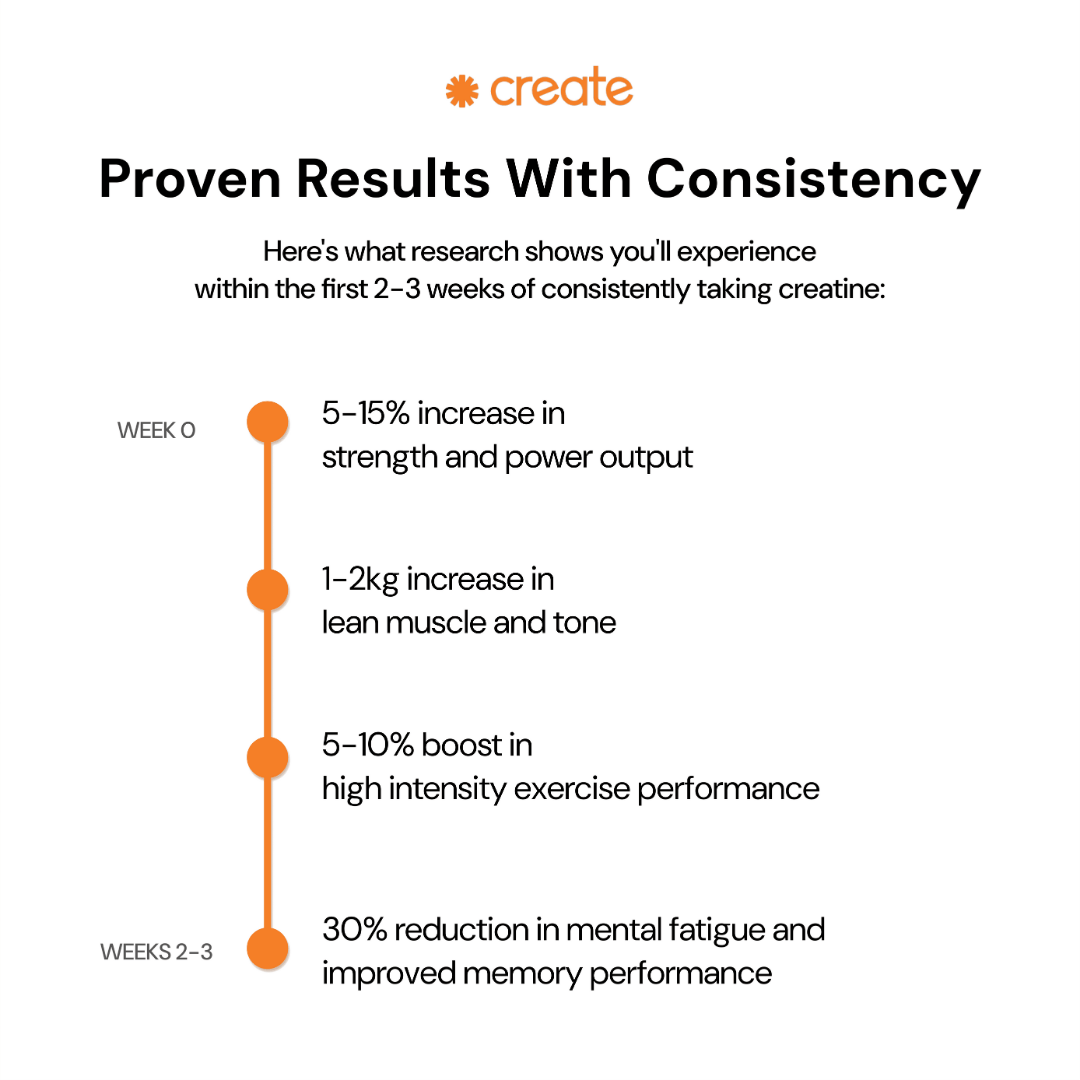
Backed by science
Creatine monohydrate is the most researched fitness supplement on the market. Here's what the science says:
What is creatine?
Creatine is made up of three different amino acids: glycine, arginine, and methionine. Creatine is naturally produced in your body and is also consumed when eating red meat, poultry, and fish.


How does creatine work?
Creatine supplementation increases your body's stores of phosphocreatine, which is used to produce new ATP during high-intensity exercise. ATP is the energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things.
Where Does Creatine Come From?
Creatine is made up of three different amino acids: glycine, arginine, and methionine.
Creatine is naturally produced in your body and is also consumed when eating red meat, poultry, and fish.
Creatine supplementation increases your body's stores of phosphocreatine, which is used to produce new ATP during high-intensity exercise. ATP is the energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things.
Because creatine is so bio-available, absorption is just as efficacious in gummy form as it is in powder form.